rails8: solid cache 使用指南
rails8 提供的另一种缓存方案
What is Solid Cache?
这三个适配器的设计理念很简单:现代固态硬盘和 NVMe 硬盘的速度足以处理许多以前需要内存解决方案才能完成的任务。
通过利用这些高速驱动器,Rails 不再需要单独的基于 RAM 的工具,如 Redis。
本文涉及代码在这里可以找到: github 地址
| Local | Remote |
|---|---|
| Memory |
|
| Disk |
|
安装
注意,官方文档这些步骤没有写清楚,以我这里列出的为准 (时间是: 2024年11月27)

# rails8里默认已经添加
bundle add solid_cache
# tw
bin/rails css:install:tailwind
# 安装(网上很多教程里的 install:migrations 是老版本的做法)
./bin/rails solid_cache:install
# 这一步有可能不需要
mkdir -p db/cache_migrate
# 创建 migration
$ rails generate migration CreateSolidCacheTable --database=cache
# 将上面步骤里 `solid_cache:install` 的东西 copy 进去,然后 migrate
$ rails db:migrate开发/生产环境配置 database.yml
- 注意在 dev 环境需要开启
rails dev:cache功能,否则没有反应 - 定义2个数据库,好处是如果备份,不用备份缓存数据库了
# SQLite. Versions 3.8.0 and up are supported.
# gem install sqlite3
#
# Ensure the SQLite 3 gem is defined in your Gemfile
# gem "sqlite3"
#
default: &default
adapter: sqlite3
pool: <%= ENV.fetch("RAILS_MAX_THREADS") { 5 } %>
timeout: 5000
development:
primary:
<<: *default
database: storage/development.sqlite3
# database: path/to/persistent/storage/development.sqlite3
cache:
<<: *default
# database: path/to/persistent/storage/development_cache.sqlite3
migrations_paths: db/cache_migrate
database: storage/development_cache.sqlite3
# SQLite3 write its data on the local filesystem, as such it requires
# persistent disks. If you are deploying to a managed service, you should
# make sure it provides disk persistence, as many don't.
#
# Similarly, if you deploy your application as a Docker container, you must
# ensure the database is located in a persisted volume.
production:
primary:
<<: *default
# database: path/to/persistent/storage/production.sqlite3
cache:
<<: *default
# database: path/to/persistent/storage/production_cache.sqlite3
migrations_paths: db/cache_migrate自身缓存配置 config/cache.yml
此段为默认配置,没有修改
default: &default
store_options:
# Cap age of oldest cache entry to fulfill retention policies
# max_age: <%= 60.days.to_i %>
max_size: <%= 256.megabytes %>
namespace: <%= Rails.env %>
development:
<<: *default
test:
<<: *default
production:
database: cache
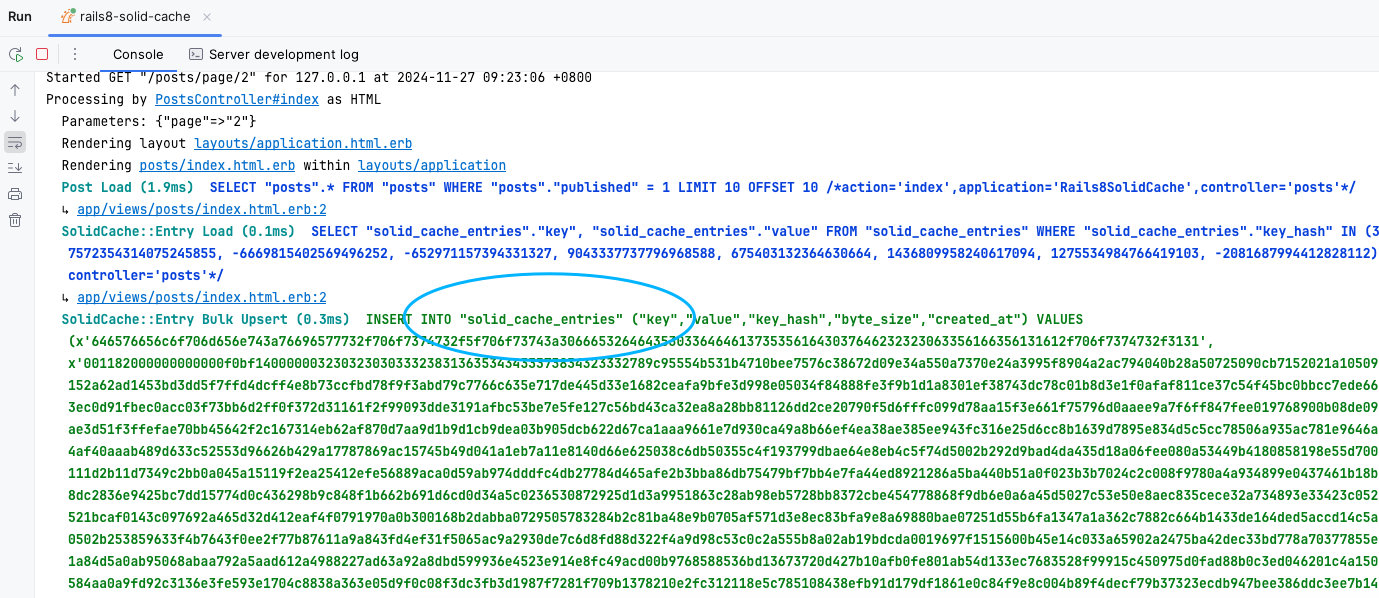
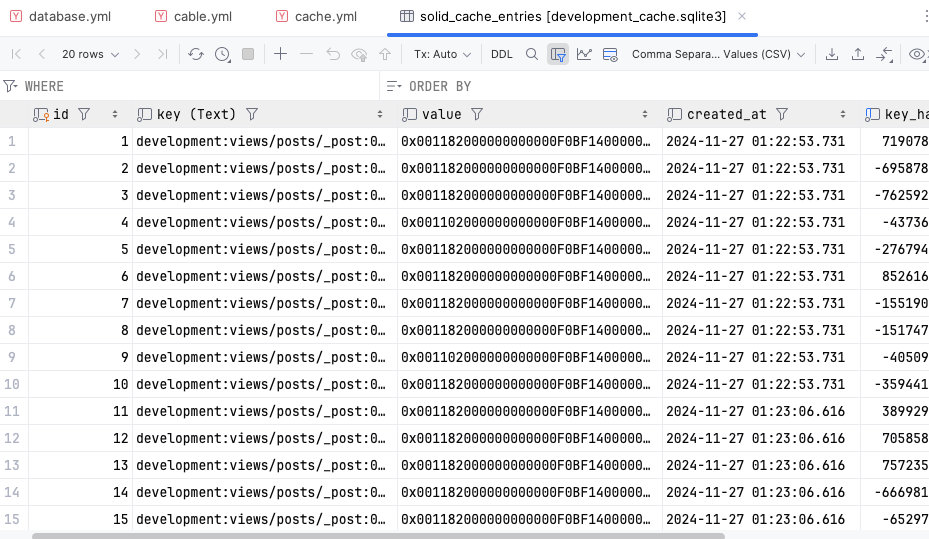
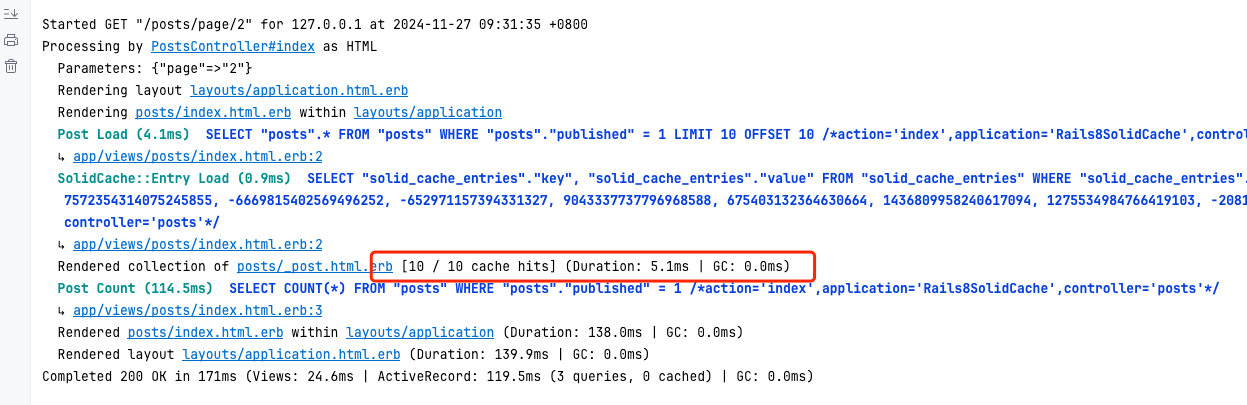
<<: *default测试有没有成功